功能权限
#👍 相关视频教程
#1. RBAC 权限模型
系统采用 RBAC 权限模型,全称是 Role-Based Access Control 基于角色的访问控制。
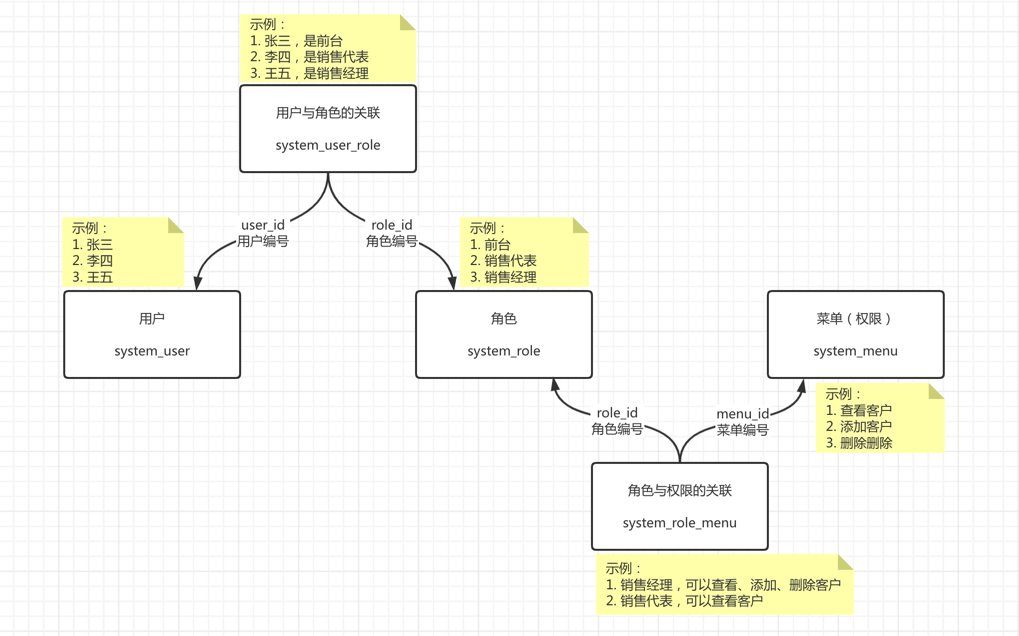
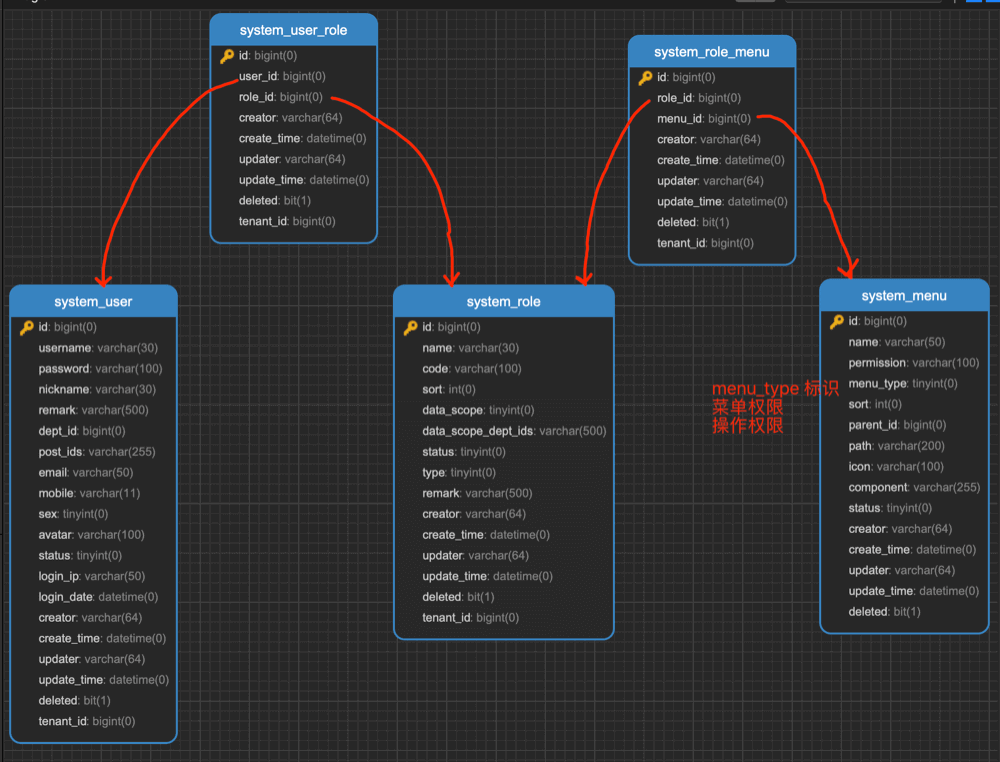
简单来说,每个用户拥有若干角色,每个角色拥有若干个菜单,菜单中存在菜单权限、按钮权限。这样,就形成了 “用户<->角色<->菜单” 的授权模型。 在这种模型中,用户与角色、角色与菜单之间构成了多对多的关系,如下图:
#2. Token 认证机制
安全框架使用的是 Spring Security + Token 方案,整体流程如下图所示:
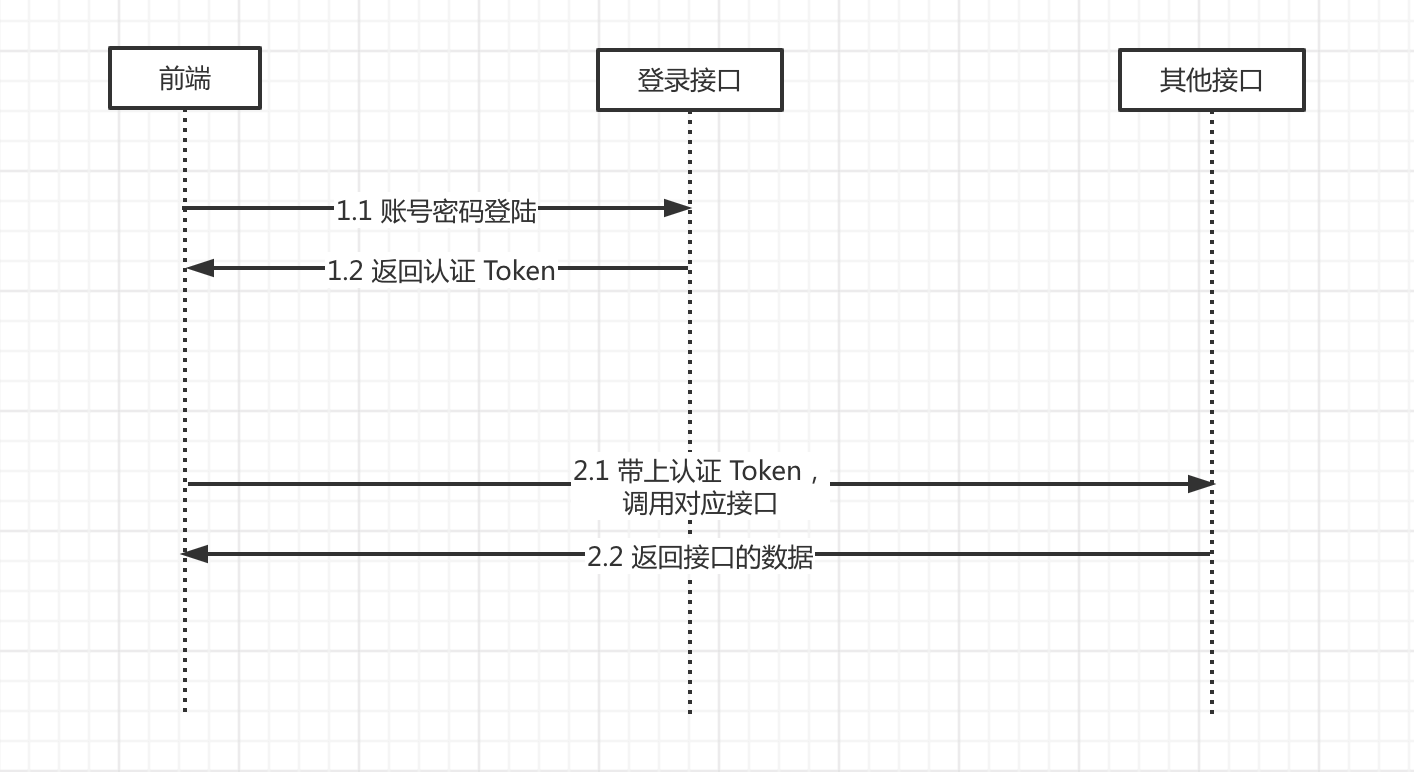
① 前端调用登录接口,使用账号密码获得到认证 Token。响应示例如下:
{
"code":0,
"msg":"",
"data":{
"token":"d2a3cdbc6c53470db67a582bd115103f"
}}疑问:为什么不使用 Spring Security 内置的表单登录?
Spring Security 的登录拓展起来不方便,例如说验证码、三方登录等等。
Token 存储在数据库中,对应 system_oauth2_access_token 访问令牌表的 id 字段。考虑到访问的性能,缓存在 Redis 的 oauth2_access_token:%s 键中。
疑问:为什么不使用 JWT(JSON Web Token)?
JWT 是无状态的,无法实现 Token 的作废,例如说用户登出系统、修改密码等等场景。
推荐阅读 《还分不清 Cookie、Session、Token、JWT?》 文章。
默认配置下,Token 有效期为 30 天,可通过 system_oauth2_client 表中 client_id = default 的记录进行自定义:

修改
access_token_validity_seconds字段,设置访问令牌的过期时间,默认 1800 秒 = 30 分钟修改
refresh_token_validity_seconds字段,设置刷新令牌的过期时间,默认 43200 秒 = 30 天
② 前端调用其它接口,需要在请求头带上 Token 进行访问。请求头格式如下:
### Authorization: Bearer 登录时返回的 TokenAuthorization: Bearer d2a3cdbc6c53470db67a582bd115103f
具体的代码实现,可见 TokenAuthenticationFilter 过滤器
考虑到使用 Postman、Swagger 调试接口方便,提供了 Token 的模拟机制。请求头格式如下:
### Authorization: Bearer test用户编号Authorization: Bearer test1
其中 "test" 可自定义,配置项如下:
### application-local.yamlyudao: security: mock-enable: true # 是否开启 Token 的模拟机制 mock-secret: test # Token 模拟机制的 Token 前缀
#3. 权限注解
#3.1 @PreAuthorize 注解
@PreAuthorize 是 Spring Security 内置的前置权限注解,添加在接口方法上,声明需要的权限,实现访问权限的控制。
① 基于【权限标识】的权限控制
权限标识,对应 system_menu 表的 permission 字段,推荐格式为 ${系统}:${模块}:${操作},例如说 system:admin:add 标识 system 服务的添加管理员。
使用示例如下:
// 符合 system:user:list 权限要求@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermission('system:user:list')")// 符合 system:user:add 或 system:user:edit 权限要求即可@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasAnyPermissions('system:user:add,system:user:edit')")② 基于【角色标识】的权限控制
权限标识,对应 system_role 表的 code 字段, 例如说 super_admin 超级管理员、tenant_admin 租户管理员。
使用示例如下:
// 属于 user 角色@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasRole('user')")// 属于 user 或者 admin 之一@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasAnyRoles('user,admin')")实现原理是什么?
当 @PreAuthorize 注解里的 Spring EL 表达式返回 false 时,表示没有权限。
而 @PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermission('system:user:list')") 表示调用 Bean 名字为 ss 的 #hasPermission(...) 方法,方法参数为 "system:user:list" 字符串。ss 对应的 Bean 是 PermissionServiceImpl 类,所以你只需要去看该方法的实现代码 。
#3.2 @PreAuthenticated 注解
@PreAuthenticated 是项目自定义的认证注解,添加在接口方法上,声明登录的用户才允许访问。
主要使用场景是,针对用户 App 的 /app-app/** 的 RESTful API 接口,默认是无需登录的,通过 @PreAuthenticated 声明它需要进行登录。使用示例如下:
// AppAuthController.java@PostMapping("/update-password")@Operation(summary = "修改用户密码", description = "用户修改密码时使用")@PreAuthenticatedpublic CommonResult<Boolean> updatePassword(@RequestBody @Valid AppAuthUpdatePasswordReqVO reqVO) {
// ... 省略代码}具体的代码实现,可见 PreAuthenticatedAspect 类。
#4. 自定义权限配置
默认配置下,管理后台的 /admin-api/** 所有 API 接口都必须登录后才允许访问,用户 App 的 /app-api/** 所有 API 接口无需登录就可以访问。
如下想要自定义权限配置,设置定义 API 接口可以匿名(不登录)进行访问,可以通过下面三种方式:
#4.1 方式一:自定义 AuthorizeRequestsCustomizer 实现
每个 Maven Module 可以实现自定义的 AuthorizeRequestsCustomizer Bean,额外定义每个 Module 的 API 接口的访问规则。例如说 yudao-module-infra 模块的 SecurityConfiguration 类,代码如下:
@Configuration("infraSecurityConfiguration")public class SecurityConfiguration {
@Value("${spring.boot.admin.context-path:''}")
private String adminSeverContextPath;
@Bean("infraAuthorizeRequestsCustomizer")
public AuthorizeRequestsCustomizer authorizeRequestsCustomizer() {
return new AuthorizeRequestsCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry registry) {
// Swagger 接口文档
registry.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/webjars/**").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/*/api-docs").anonymous();
// Spring Boot Actuator 的安全配置
registry.antMatchers("/actuator").anonymous()
.antMatchers("/actuator/**").anonymous();
// Druid 监控
registry.antMatchers("/druid/**").anonymous();
// Spring Boot Admin Server 的安全配置
registry.antMatchers(adminSeverContextPath).anonymous()
.antMatchers(adminSeverContextPath + "/**").anonymous();
}
};
}}友情提示
permitAll()方法:所有用户可以任意访问,包括带上 Token 访问anonymous()方法:匿名用户可以任意访问,带上 Token 访问会报错
如果你对 Spring Security 了解不多,可以阅读艿艿写的 《芋道 Spring Boot 安全框架 Spring Security 入门 》 文章。
#4.2 方式二:@PermitAll 注解
在 API 接口上添加 @PermitAll 注解,示例如下:
// FileController.java@GetMapping("/{configId}/get/{path}")@PermitAllpublic void getFileContent(HttpServletResponse response,
@PathVariable("configId") Long configId,
@PathVariable("path") String path) throws Exception {
// ...}#4.3 方式三:yudao.security.permit-all-urls 配置项
在 application.yaml 配置文件,通过 yudao.security.permit-all-urls 配置项设置,示例如下:
yudao: security: permit-all-urls: - /admin-ui/** # /resources/admin-ui 目录下的静态资源 - /admin-api/xxx/yyy
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表xx立场。
本文系作者授权xxx发表,未经许可,不得转载。


发表评论